Individual Project (iP):
Team Project (tP):
In a smaller system, design of the entire system can be shown in one place.
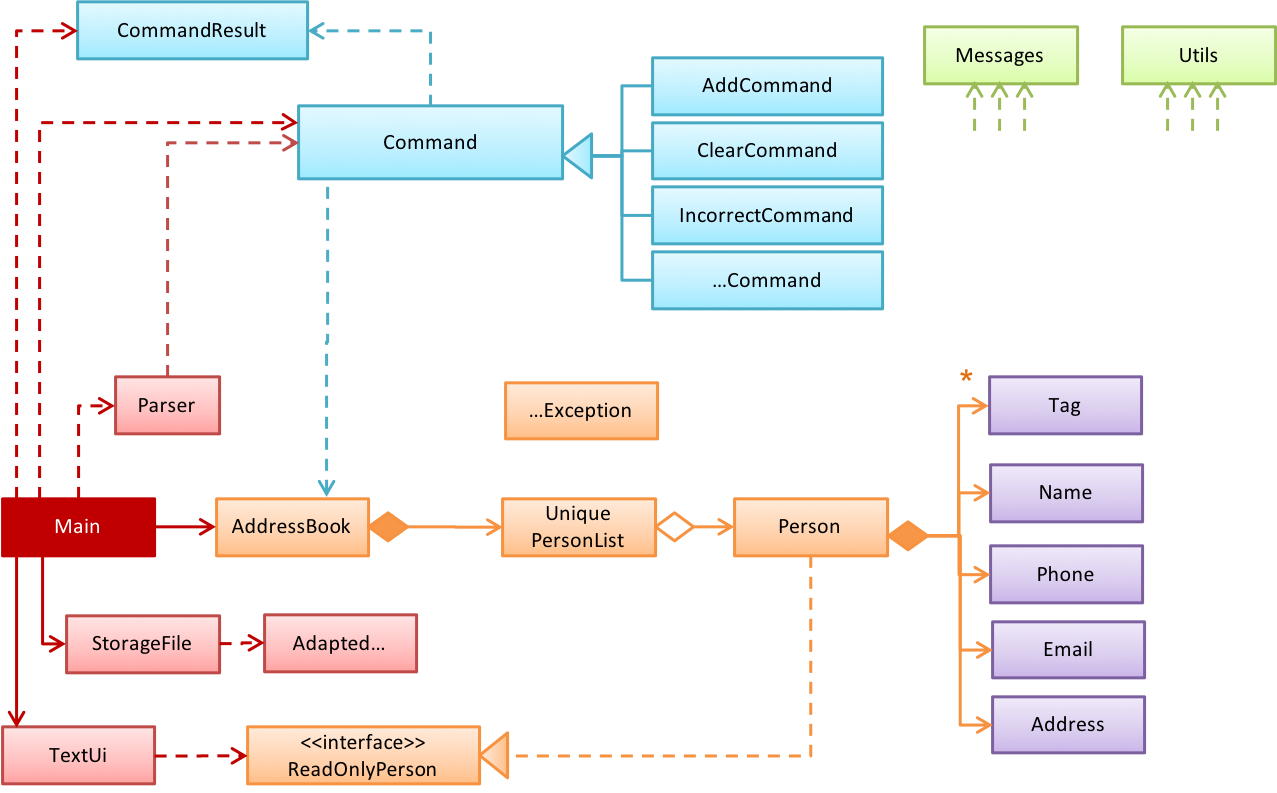
This class diagram of se-edu/addressbook-level2 depicts the design of the entire software.
Design of bigger systems needs to be done/shown at multiple levels.
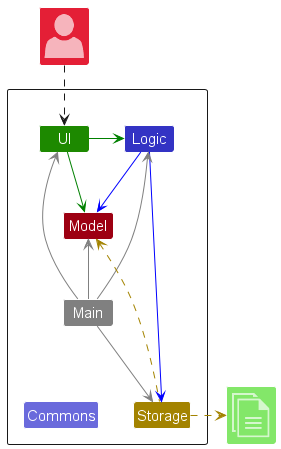
This architecture diagram of se-edu/addressbook-level3 depicts the high-level design of the software.
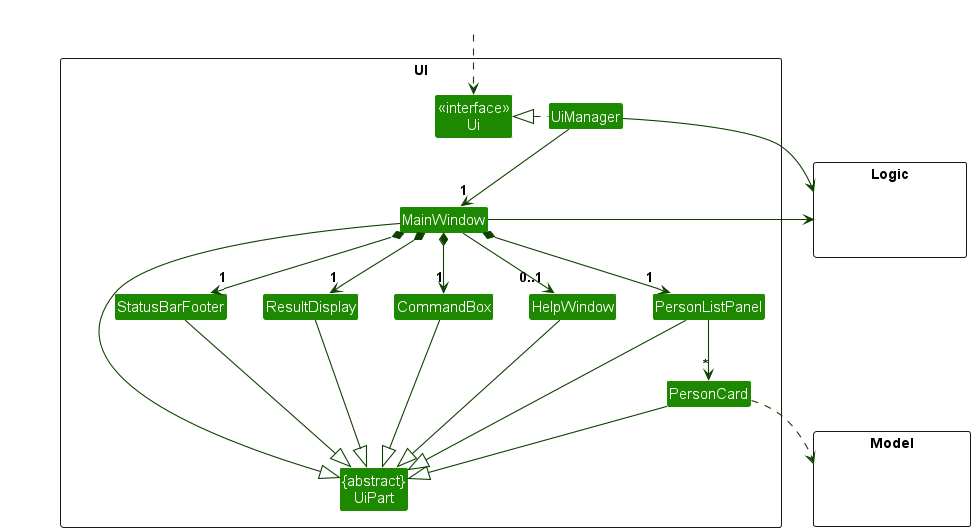
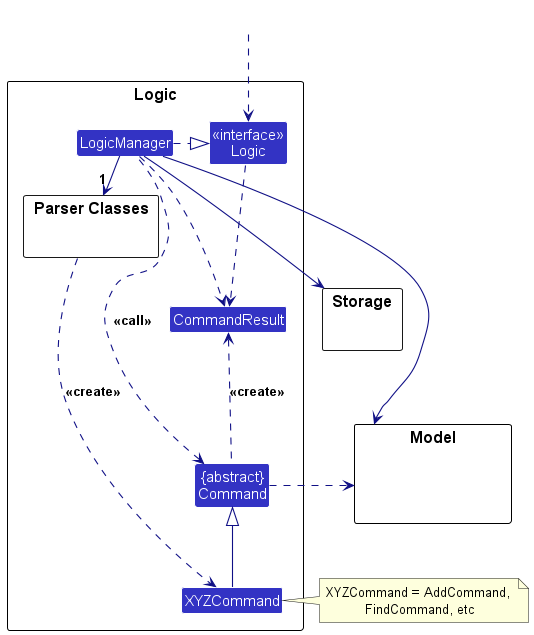
Here are examples of lower level designs of some components of the same software:
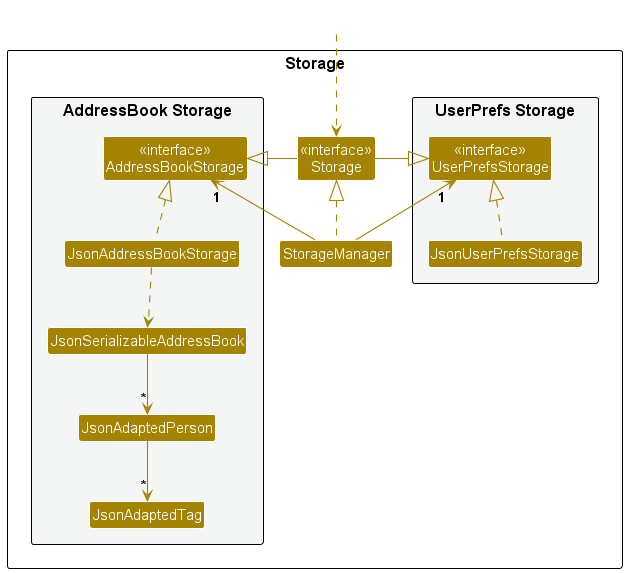
Multi-level design can be done in a top-down manner, bottom-up manner, or as a mix.
- Top-down: Design the high-level design first and flesh out the lower levels later. This is especially useful when designing big and novel systems where the high-level design needs to be stable before lower levels can be designed.
- Bottom-up: Design lower level components first and put them together to create the higher-level systems later. This is not usually scalable for bigger systems. One instance where this approach might work is when designing a variations of an existing system or re-purposing existing components to build a new system.
- Mix: Design the top levels using the top-down approach but switch to a bottom-up approach when designing the bottom levels.
Top-down design is better than bottom-up design.
False
Explanation: Not necessarily. It depends on the situation. Bottom-up design may be preferable when there are lot of existing components we want to reuse.
Agile design can be contrasted with full upfront design in the following way:
Agile designs are emergent, they’re not defined up front. Your overall system design will emerge over time, evolving to fulfill new requirements and take advantage of new technologies as appropriate. Although you will often do some initial architectural modeling at the very beginning of a project, this will be just enough to get your team going. This approach does not produce a fully documented set of models in place before you may begin coding. -- adapted from agilemodeling.com
Agile design camp expects the design to change over the product’s lifetime.
True
Explanation: Yes, that is why they do not believe in spending too much time creating a detailed and full design at the very beginning. However, the architecture is expected to remain relatively stable even in the agile design approach.